Fast Facts
Background
Grass carp have historically been used by resource managers as a means of combating nuisance aquatic vegetation in ponds and lakes in the United States. They are still legal for such use in states outside of the Great Lakes basin. By the mid-1970s, this species had been stocked in at least 45 states.
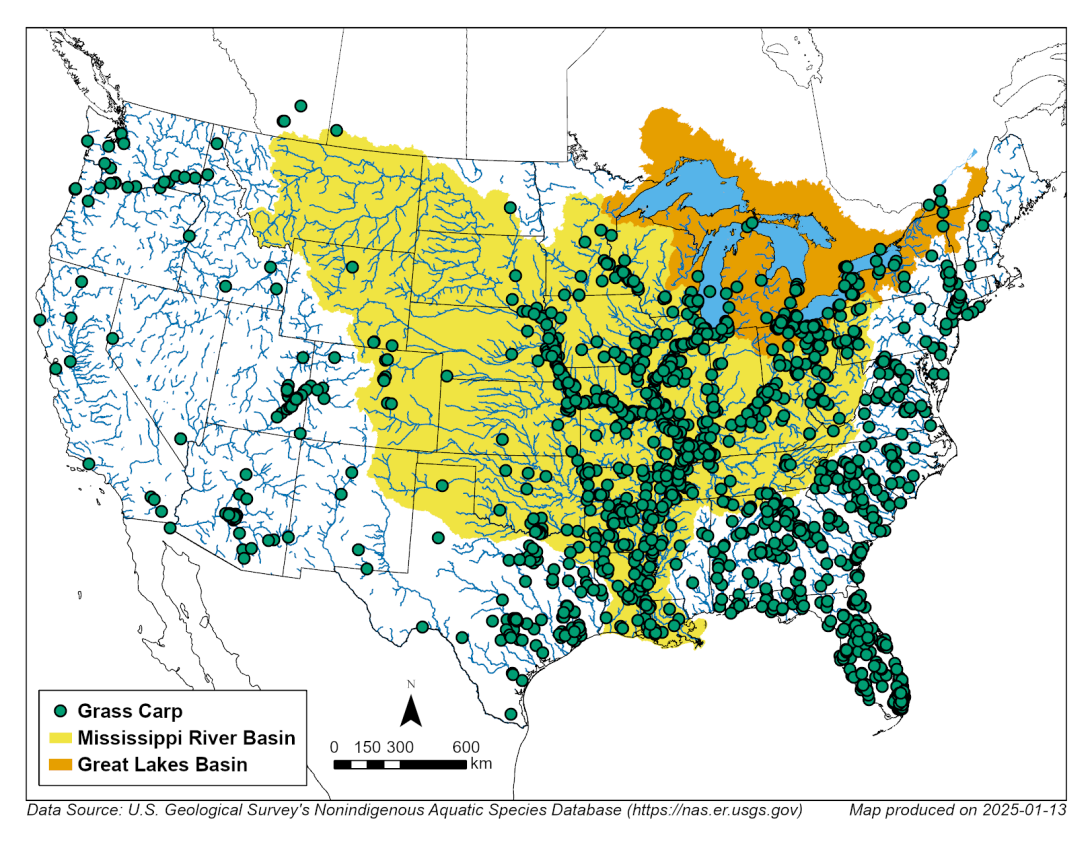
Grass carp are widely distributed throughout much of the United States. Populations of grass carp are now reproducing in major rivers near the Great Lakes including the Mississippi, Missouri, and Ohio rivers and many other smaller tributaries. Grass Carp are present within the Illinois Waterway and are occasionally removed from the Chicago Area Waterway System during Seasonal Intensive Monitoring activities. They have been detected in all of the Great Lakes except Lake Superior and are regularly detected in Lake Erie. Reproduction of grass carp populations in tributaries of the western basin of Lake Erie has also been detected.
Physical Description
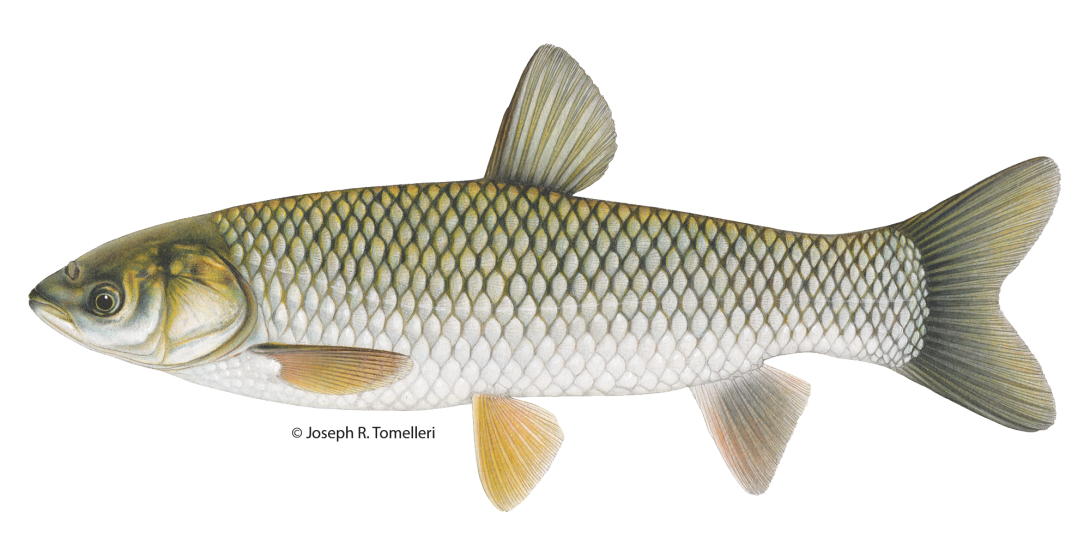
The body of a grass carp is oblong shaped with a slightly flattened head and moderately small eyes centered on the side of the head. They are covered with large overlapping scales, and coloration varies from blackish to olive-brown with brassy or silvery-white on the sides and belly. Scales on the back and sides are outlined by pigment giving a cross-hatched effect.
Preferred Habitat
Grass carp prefer large, slow flowing water bodies and spawn in large rivers with moderate currents. Egg survival and larval development is best in waters between 70° and 77° Fahrenheit, but adults can tolerate water temperatures ranging from 32° to 100° Fahrenheit.
Diet
Grass carp feed primarily on aquatic plants but can also consume detritus, insects, small fish, earthworms and other invertebrates in the absence of aquatic vegetation. Grass carp in the wild can consume anywhere from 20% to 100% of their body weight per day depending on the life stage and size of the fish, type of vegetation and water temperature. By eating such huge quantities of plant plants, grass carp can significantly alter habitat by reducing food sources, shelter and spawning areas for native fish. Also, because they can only digest about half of the plant material that they consume each day, the remaining material is expelled into the water, enriching it with nutrients which promotes algal blooms.
Size
Grass carp mature between 3 and 6 years, but it can take them more than a decade to grow to a maximum size of more than 80 pounds.
Historical Occurrence